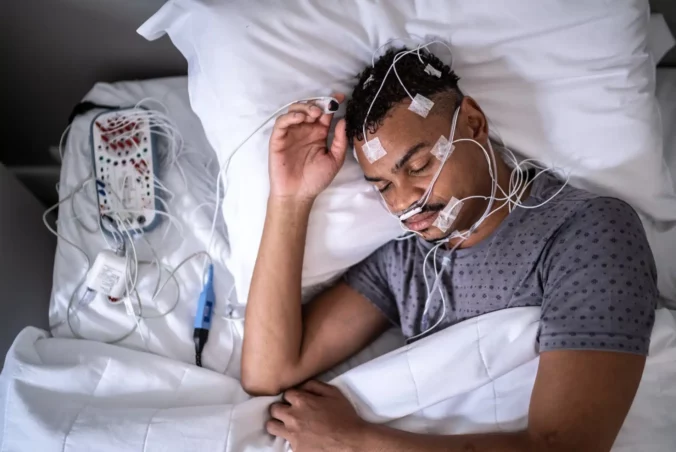
Understanding the basics of sleep studies
Sleep studies, known medically as polysomnography, are fundamental assessments that provide invaluable insights into how we sleep. They involve monitoring various physiological parameters while the individual sleeps, typically in a specialised laboratory environment. With advanced technology, sleep studies can capture detailed data that aids clinicians in understanding sleep patterns, disorders, and overall sleep quality.
Many people may wonder why these studies are necessary. While sleep might seem like a simple, natural act, it is actually quite complex. Understanding the intricacies of our sleep can reveal much about our health and well-being, leading to better treatment options for those who suffer from sleep-related issues.
What is a sleep study?
A sleep study is a comprehensive evaluation that records various bodily functions while you sleep. This includes observing brain activity, eye movements, heart rate, breathing patterns, and muscle activity. By employing this data, healthcare providers can assess whether an individual is experiencing any disorders that disrupt normal sleep.
Thus, prioritising sleep hygiene and addressing sleep disorders can lead to significant improvements in overall health and longevity. A comprehensive understanding of sleep study results serves as a critical foundation for achieving better sleep and enhancing quality of life.
Typically, these studies are conducted overnight and monitored by a sleep technician. The gathered data is then analysed by a sleep specialist who can identify any irregularities or abnormalities in sleep patterns.
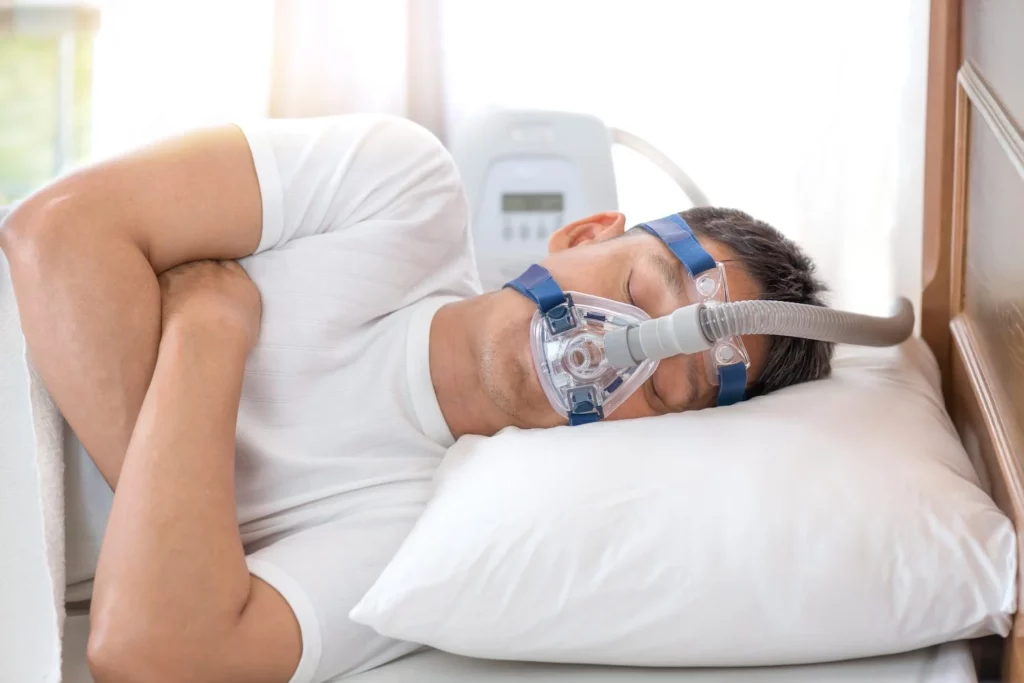

Why are sleep studies important?
These studies play a pivotal role in diagnosing and understanding different sleep disorders. Conditions such as sleep apnoea, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
By obtaining a clear picture of one’s sleep patterns through a study, clinicians can propose effective treatment plans tailored to the patient’s needs. This awareness can ultimately lead to improved health outcomes and restored sleep quality.
To read about sleep study Penrith click here.
The science behind sleep studies
To fully understand sleep studies, it is essential to delve into the science of sleep. Our sleep is divided into stages, and each plays a crucial role in maintaining our physical and mental health. The journey from light sleep to deep sleep and REM sleep underscores the intricate web of bodily functions that occur overnight.
The stages of sleep
There are typically five stages of sleep, ranging from light sleep when we first doze off, to deep sleep, and finally REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep. Light sleep is where we transition into slumber, while deep sleep is critical for physical recovery and growth. Conversely, REM sleep is when dreaming occurs, and it plays a vital role in memory consolidation and emotional regulation.
A healthy sleep cycle includes multiple iterations of these stages, each contributing to restorative processes. Sleep studies are designed to capture these variations and help identify if someone regularly cycles through these stages or if they experience disruptions. Read more about variations at https://evolution.berkeley.edu/glossary/variation/
The role of brain waves in sleep
During a sleep study, brain waves are measured using electroencephalography (EEG). Different brain wave patterns signify different sleep stages. For example, slow-wave sleep is marked by high-amplitude, low-frequency brain waves, which indicate deep restorative sleep.
By examining these brain waves, sleep specialists can assess how well an individual transitions between sleep stages, thereby identifying potential sleep disorders that might be causing issues.
Deciphering your sleep study results
Once the sleep study is completed, the results can seem overwhelming. However, breaking them down can make interpretation easier and more comprehensible. Each aspect of the report serves a distinct purpose in understanding the quality of your sleep.
Understanding sleep latency
Sleep latency refers to the amount of time it takes for an individual to fall asleep after lying down. It provides insights into how quickly you transition from being awake to being asleep. A long sleep latency may indicate issues such as insomnia, where stress and anxiety can prevent a person from drifting off.
Conversely, abnormally short sleep latency could suggest excessive daytime sleepiness or other sleep disorders, prompting further investigation into the underlying causes. Click here to read more about investigation.
Interpreting sleep efficiency
Sleep efficiency is a crucial metric derived from the sleep study results. It’s calculated by dividing the total amount of time spent asleep by the total time spent in bed. A higher sleep efficiency percentage indicates a more restful night, while lower figures may highlight disturbances or the inability to maintain sleep.
By scrutinising this statistic, individuals can better understand their sleep patterns and address any environmental or lifestyle factors that might be interrupting their sleep.
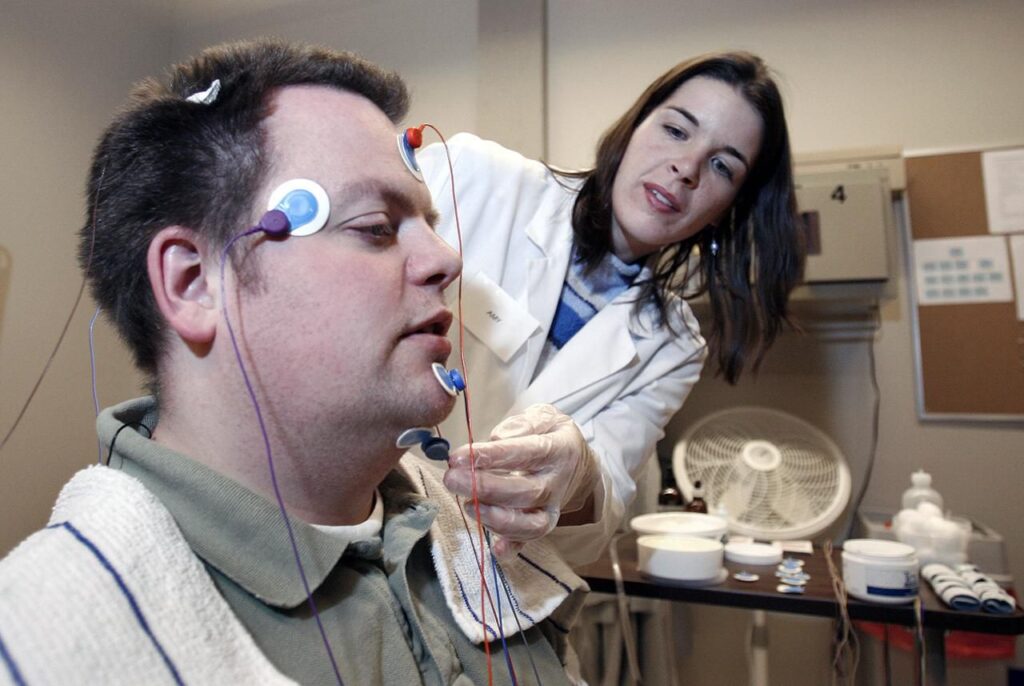
The significance of sleep cycles and interruptions
Sleep studies also assess the number of awakenings and interruptions during the night. Frequent disruptions can have a detrimental effect on sleep quality and overall health. For instance, waking up multiple times may prevent an individual from reaching the restorative sleep stages, leading to fatigue and other health issues.
Understanding these interruptions can help shape lifestyle changes that promote a more restful sleep environment, from optimising bedroom conditions to managing outside noise.
Common sleep disorders identified through sleep studies
Given the significance of sleep studies, they serve as an essential diagnostic tool for various sleep disorders. Gaining clarity on these disorders can empower individuals to seek appropriate treatments and improve their quality of life.
Sleep apnoea and its indicators
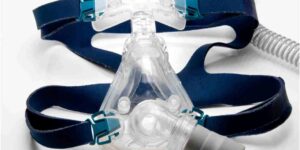
One of the most common disorders identified is sleep apnoea, characterised by pauses in breathing during sleep. Symptoms may include loud snoring, choking during the night, and excessive daytime fatigue. Sleep studies help reveal the frequency and duration of these breathing pauses, guiding potential treatment options.
Identifying sleep apnoea can lead to lifestyle changes, the use of CPAP machines, or other interventions, all aimed at enhancing respiratory function during sleep.
Insomnia and its signs in sleep studies
Insomnia is another prevalent sleep disorder that can often be diagnosed through sleep studies. Individuals with insomnia experience difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep, which can be exacerbated by various factors, including stress and anxiety. The study results can highlight patterns of wakefulness and help determine effective interventions.
Techniques ranging from cognitive behavioural therapy to lifestyle modifications can be utilised to combat insomnia and restore healthy sleep habits.
Restless leg syndrome and periodic limb movement disorder
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) and periodic limb movement disorder (PLMD) can also be diagnosed through polysomnography. RLS creates an uncontrollable urge to move one’s legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. PLMD involves involuntary leg movements during sleep, leading to disruptions. Identifying these conditions can help in formulating appropriate treatment plans that alleviate symptoms and improve overall sleep quality.
The impact of sleep quality on overall health
Ultimately, the quality of one’s sleep holds significant implications for overall health. It influences not just how we feel during the day, but also our mental and physical well-being.
Sleep and mental health
Research indicates a strong connection between sleep and mental health. Poor sleep quality can exacerbate conditions such as depression and anxiety, while also reducing cognitive function. Equally, improving sleep can often lead to enhanced mental clarity and emotional stability.
Recognising and addressing sleep issues can be a vital step in improving mental health, illustrating the importance of seeking assistance when necessary.
Sleep and physical health
The role of sleep in physical health is equally vital. Quality sleep is associated with better immune function, weight management, and cardiovascular health. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.